Proper maintenance of quality control strains is essential for ensuring acceptable performance. Most strains produced by Microbiologics can be used for up to a month after reconstitution when correctly maintained. Follow these best practices and our maintenance plan below to preserve the viability, purity, and genotypic and phenotypic characteristics of your strains from Microbiologics.
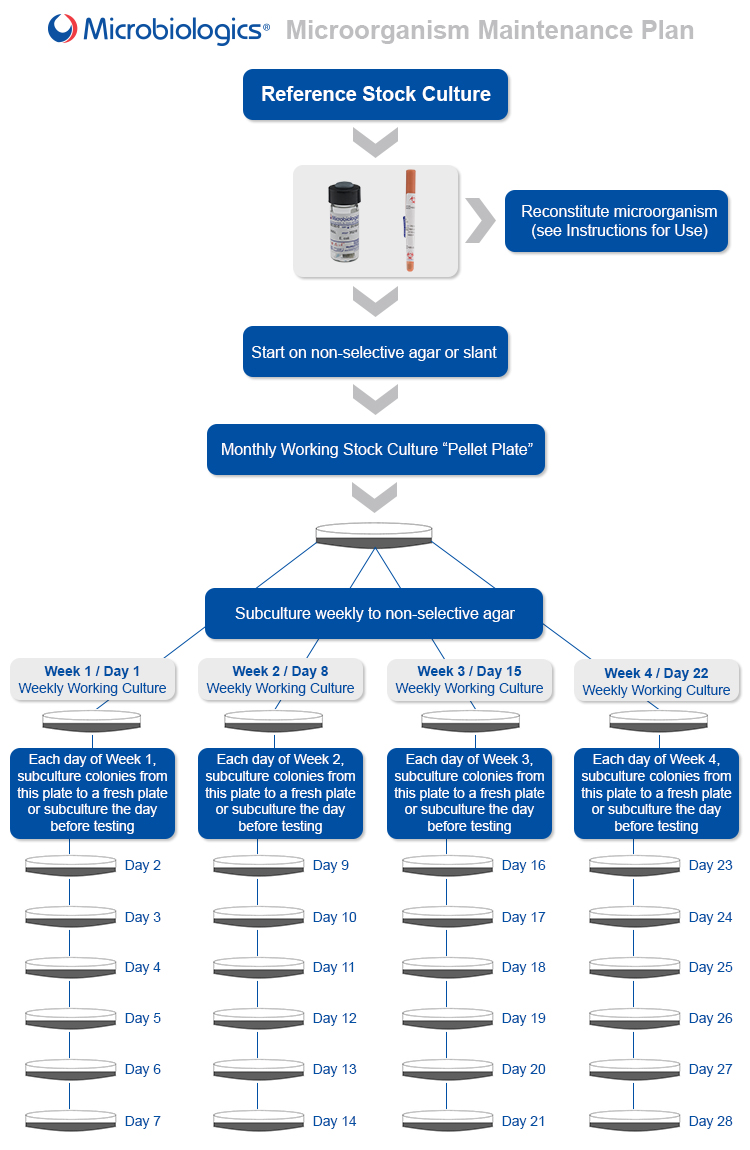
Getting Started
- Microbiologics microorganism strains should be started on a non-selective agar such as Tryptic Soy Agar or Sheep Blood Agar. Broth is not recommended because contaminants can be easily introduced. Our Recommended Culture Methods document lists individual species media requirements. Culture method for each strain can also be found on the product’s page on our website.
- To maintain the microorganism strain, follow the maintenance plan at the end of the post.
Storage of Reconstituted Microorganisms
- Most QC microorganisms can be maintained on nonselective agar plates or slants for up to four weeks at room temperature or in the refrigerator.1, 4
- Fastidious microorganisms have shorter survival periods than aerobic bacteria. These strains need to be subcultured every few days. For example, Streptococcus pneumoniae and Neisseria gonorrhoeae need to be subcultured every third day.
- We’ve found the following storage conditions to be favorable for maintenance:
| Category of Microorganism | Storage Conditions |
| Aerobic Bacteria | Store at 2°- 8°C. A few species of Bacillus remain viable for a longer period when stored at room temperature. |
| CO2 Dependent Species | Store at room temperature in a candle jar or in a container with a CO2 packet. |
| Yeast and Fungi | Store at room temperature. |
| Anaerobes | Store in anaerobic conditions at room temperature. |
| Campylobacter | Store on chocolate agar at 35°C in microaerophilic conditions. |
- Microorganisms stored at 4°C should not be used for certain tests. Always consult the manufacturer’s instructions.
- If the resuscitated culture is frozen, Microbiologics cannot guarantee the stated characteristics of the product.
Tips for Best Performance
- Do not test the original pellet plate for phenotypic characteristics or antibiotic susceptibility. This is the plate on which the lyophilized pellet was started. The organisms growing on this plate are not fully resuscitated.
- Select isolated colonies for a test. Do not test colonies from a contaminated plate.
- When possible, use microorganisms that are not more than 24 hours old for biochemical tests.
- It may be necessary to start microorganisms used for quality control of antibiotic susceptibility tests every two weeks because some microorganisms lose resistance over time.1
- Some pharmacopeia tests, such as the growth promotion test, require that strains be five passages or less from the original reference culture.3 In this case, we recommend using EZ-Accu Shot™ (quantitative and three passages from reference culture) or KWIK-STIK™ Plus strains (two passages from reference culture).
Wrapping Up
- After the fourth week, dispose of plates and start the process over with a new lyophilized pellet.
- A microorganism may be used beyond expiry date if (1) the lyophilized pellet is grown before expiry date and (2) the microorganism is not used beyond week four of the maintenance program.
Visit our website for technical documents, product FAQs, and videos. Contact our Technical Support team at techsupport@microbiologics.com or 1.320.229.7045 with questions about maintaining Microbiologics QC microorganisms.
Read Next – Dear Stanley: The Differences Between Atmospheres for Microorganism Growth
References
- CLSI M07-A10, Vol. 35 2, Methods fors Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria that Grow Aerobically: Approved Standard – Tenth Edition, Clinical Standards Laboratory Institute. April 2015.
- Microbiologics Recommended Culture Methods
- United States Pharmacopeia 38 NF 33, <61> Microbiological Examination of Nonsterile Products: Microbial Enumeration Tests. 2015
- ISO 11133, Microbiology of food, animal feed and water – Preparation, production, storage and performance testing of culture media. First edition 2014-05-15





0 Comments
Trackbacks/Pingbacks